What Are the Early Signs of Hearing Loss in Children?
Worried about your child’s hearing? Early signs of hearing loss can be subtle but spotting them early makes a huge difference! But how can you recognize the early signs? This guide covers key indicators, evidence-based research, and steps to take if you suspect your child has hearing difficulties.
Why Is Early Detection of Hearing Loss Important?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 34 million children worldwide have disabling hearing loss, and 60% of cases are preventable with early detection and treatment. Undiagnosed hearing loss can lead to delays in speech, learning, and social development.
The earlier hearing loss is identified and treated, the better the chances are for a child to develop normal language skills and keep up with their peers. Early intervention often includes hearing aids, speech therapy, or other supportive measures.
Common Early Signs of Hearing Loss in Children
Hearing loss doesn’t always mean complete deafness; it can range from mild to severe. Here are some signs parents and caregivers should watch for:
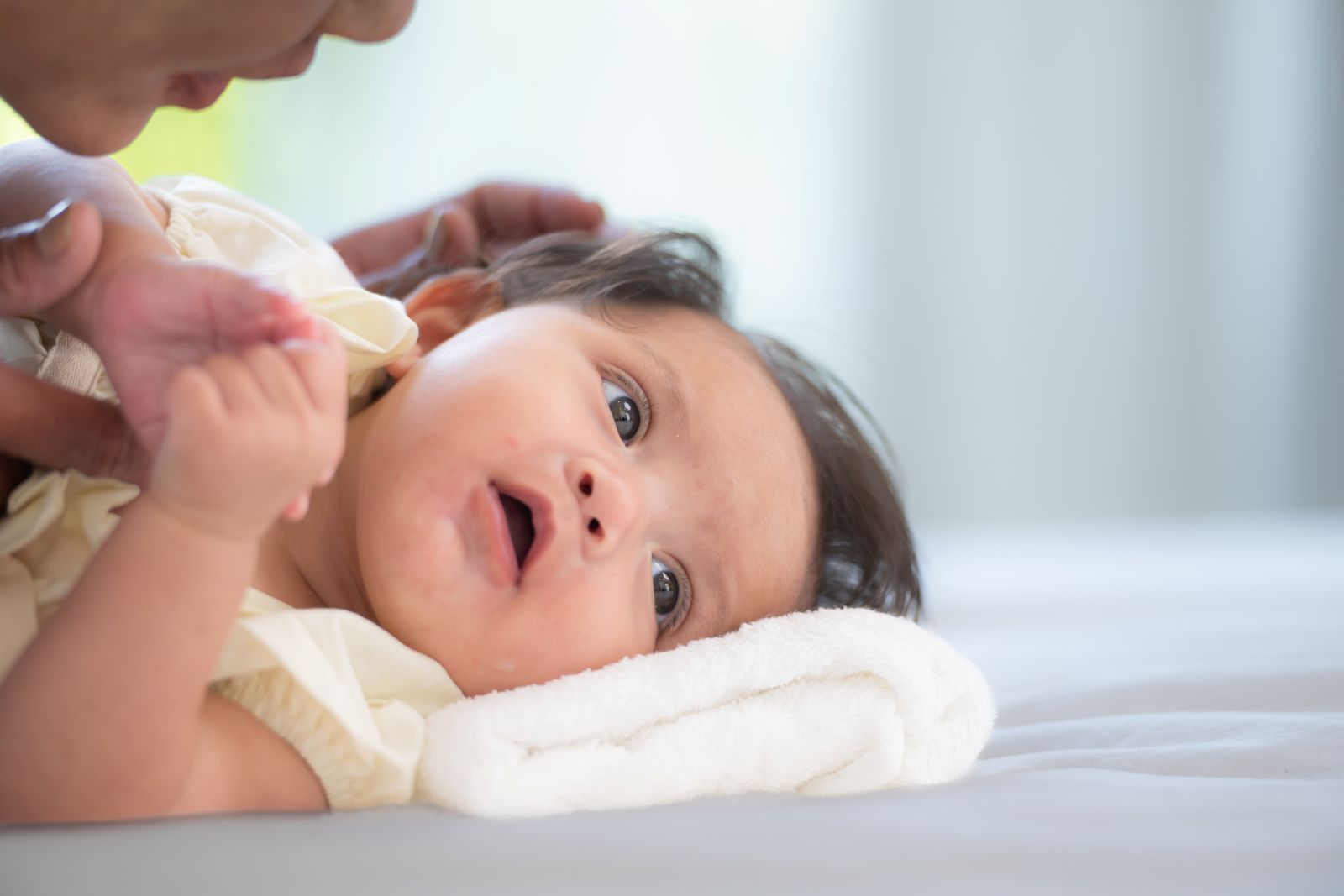
In Infants (0-12 Months)
- No startle response to loud noises (e.g., clapping, door slamming).
- Does not turn head toward sounds by 6 months.
- Lack of babbling by 7-9 months.
- Does not respond to their name by 9-12 months.
- Sleeps through loud noises that typically wake other babies.
In Toddlers (1-3 Years)
- Speech delays (e.g., not saying simple words like "mama" or "dada" by 15 months).
- Frequent ear infections, which can cause temporary hearing loss.
- Does not follow simple commands (e.g., "Come here" or "Give me the toy").
- Prefers louder volumes on TV or electronic devices.
- Appears inattentive or frustrated when listening.
In Preschool & School-Age Children (3+ Years)
- Speech is unclear or difficult to understand.
- Frequently asks "What?" or "Huh?"
- Struggles in noisy environments (e.g., classrooms).
- Academic difficulties, especially in reading and language-based subjects.
- Social withdrawal or reluctance to engage in conversations.
Key Fact: The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders states that 2-3 out of every 1,000 children in the U.S. are born with detectable hearing loss (NIDCD, 2024).
What Causes Hearing Loss in Children?
Hearing loss in children can result from a variety of factors, including:
- Genetic causes: Accounting for 40-50% of cases, according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA).
- Prenatal infections: Such as cytomegalovirus (CMV) and rubella, which can affect hearing before birth.
- Birth complications: Including low birth weight, premature delivery, or oxygen deprivation during birth.
- Chronic ear infections: Repeated middle ear infections (otitis media) can impact hearing over time.
- Exposure to loud noises: Prolonged or frequent exposure to loud sounds, like headphone use at high volumes, can damage hearing.
Understanding these causes helps in early detection and prevention to protect your child’s hearing health.
What Should You Do If You Suspect Hearing Loss?
If you notice any of these signs or have concerns about your child’s hearing:
- Schedule a hearing test if you notice any red flags.
- Follow up with an audiologist for a comprehensive evaluation.
- Explore intervention options, such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, or speech therapy.
- Monitor ear health by treating infections promptly.
Pediatric Hearing Care You Can Trust in Connecticut
If you notice your child isn’t responding to sounds, has speech delays, or struggles in noisy places, our expert pediatric audiologists can help. At ENT Medical and Surgical Group, we offer:
✔️ Child-friendly hearing tests
✔️ Cutting-edge hearing aid technology
✔️ Caring, personalized support for your family
Don’t wait—schedule a hearing screening today! Early action gives your child the best chance to thrive.