What’s the Difference Between Adenoids and Tonsils?
Did you know that your tonsils and adenoids are the first lines of your body’s defense against infections? But even though they are both crucial parts of your immune system and are made of lymphatic tissues, there are several differences between these two with regards to their location, function, and the infections they’re more susceptible to.
Major Differences Between Adenoids and Tonsils
Location
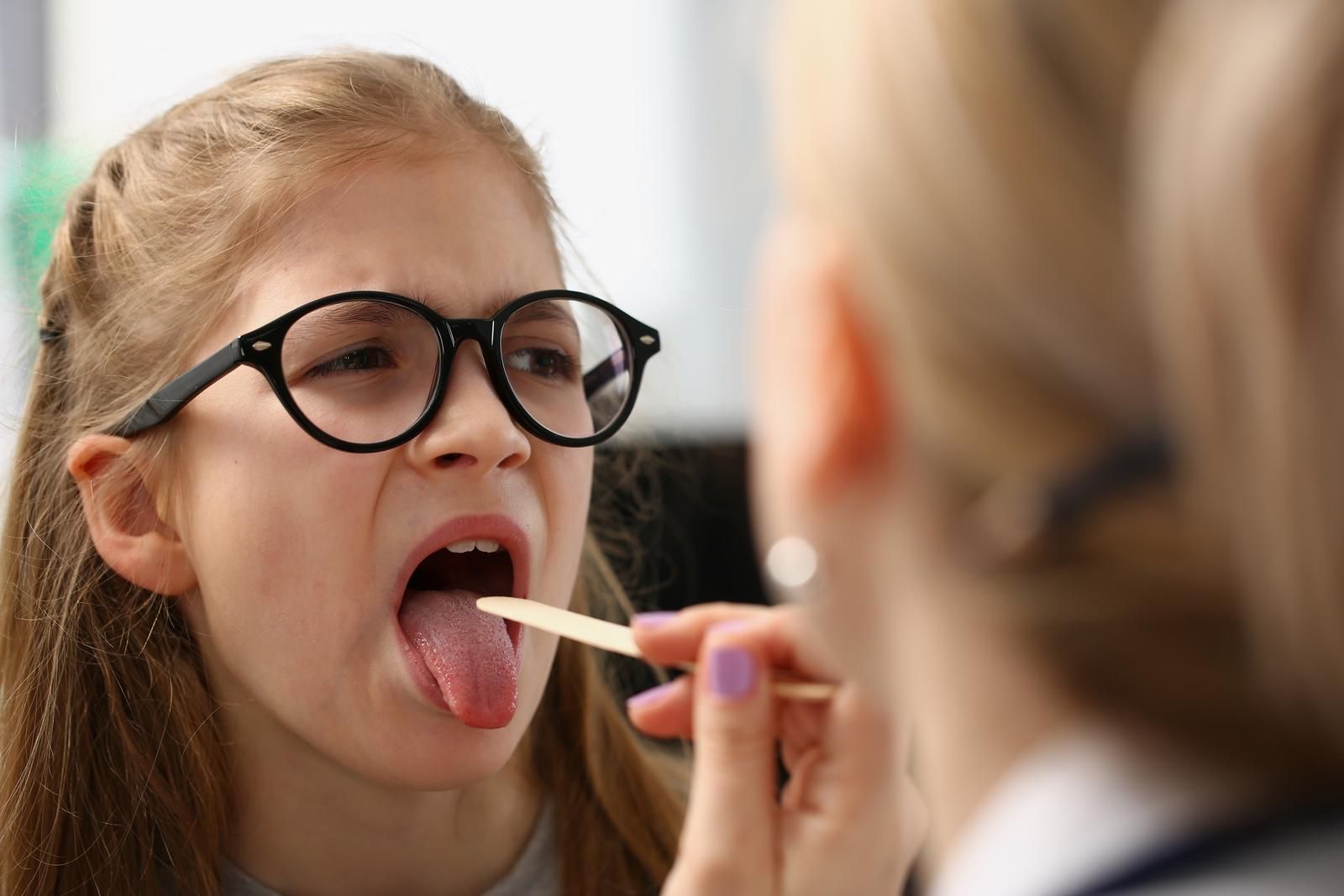
Adenoids, also known as pharyngeal tonsils, are a patch of tissue located high up in the throat, right behind the nose and soft palate. The two lumps found at the back of your throat are called tonsils, also referred to as palatine tonsils. They can be easily seen with a torchlight when you open your mouth. In contrast, adenoids are not as easily noticeable.
Function
Tonsils and Adenoids are both responsible for protecting your body from pathogens. They work together to trap bacteria, viruses, and other germs entering the body through the mouth or nose. According to a 2020 literature review, both these glands are also in charge of activating white blood cells that help fight infections.
Moreover, adenoids are also covered by a layer of mucus and hairlike structures called cilia. The mucus layer traps pollen, smoke, and other micro-particles that enter our body while the cilia work to dispel these trapped particles out the nose.
Infections and Their Treatments
As the immune system’s first line of defense, adenoids and tonsils are both susceptible to inflammation. This usually happens when they’re fighting pathogens. But some children may have enlarged adenoids and tonsils without any specific cause. However, adenoids start to shrink once a child crosses 5 years of age.
Adenoiditis:
As the name suggests, adenoiditis is an infection of the adenoids. The symptoms usually include difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring, restless sleep, stuffiness in the nose, a stubborn runny nose, swollen glands in the neck, and ear problems.
The possible complications of adenoiditis include ear infections and sinusitis. In severe cases, the infection can spread to the lungs and other parts of the respiratory system, resulting in pneumonia or bronchitis.
Your doctors might recommend an adenoidectomy, the removal of the adenoid glands, if the infections occur too frequently or are difficult to control. The procedure is performed under the influence of general anesthesia.
Tonsillectomy
Fever, sore throat accompanied by ear pain, white or yellow patches on the tonsils, redness, and swelling of the tonsils, difficulty swallowing, and bad breath are some of the symptoms your ENT doctor might look out for when diagnosing a tonsil infection.
If left untreated, tonsillitis can lead to further complications, such as a peritonsillar abscess or chronic sinus infections. If tonsillitis becomes severe or frequent, then tonsillectomy, or the surgical removal of tonsils, is the only treatment option you might have. It is also performed under the influence of general anesthesia.
As mentioned above, tonsils and adenoids are essential components of the immune system that help trap pathogens. But if either of the two is prone to frequent infections, it is best to have them removed after consulting an ENT specialist. It is a very common and straightforward procedure, and most patients return to regular life about a week after surgery.
If you’re looking for treatment options for frequent adenoiditis or tonsillitis in Hartford and New Haven, CT, get in touch with the specialists at ENT Medical and Surgical Group. Call us at (203) 752-1726 or contact us online!